NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA SPECTRUM DISORDER
Once thought to be a type of Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD) is a distinct and rare autoimmune disease of the Central Nervous System (CNS) in which the immune system attacks the optic nerve and spinal cord.
NMOSD is a rare disease identified by the presence of antibodies to aquaporin-4 (AQP4), which distinguishes it from MS.
ARE THERE THERAPIES FOR NMOSD?
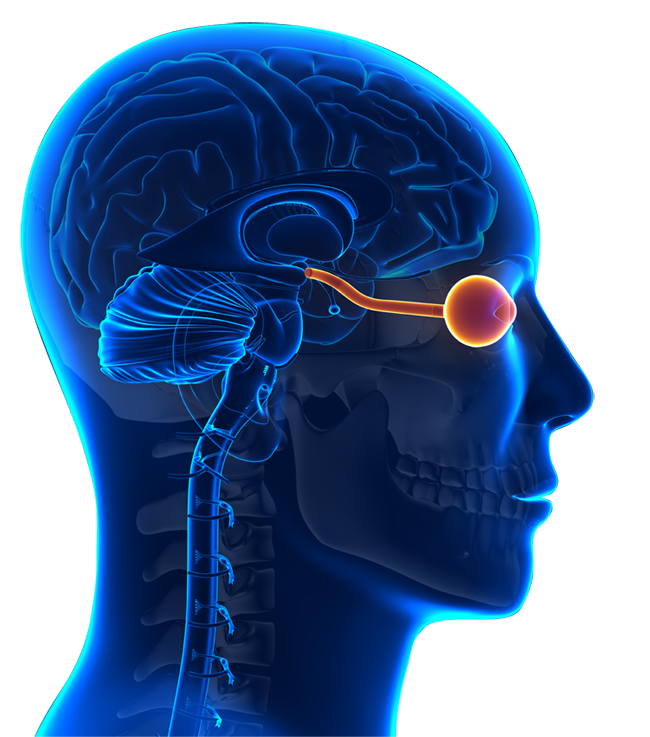
As of 2019, Soliris (Alexion) has been approved as a therapy to reduce relapses in NMOSD patients. This is an important advance because each relapse causes progressive and irreversible damage to the brain, optic nerve, and spinal cord.
Currently, no drugs exist that are able to reverses the damage.
ENDECE is developing NDC-1308 to stop progression, reverse damage, and improve function in patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD).
NMOSD SYMPTOMS
THE SYMPTOMS OF NMOSD CAN VARY FROM PERSON TO PERSON IN RELATION TO DISABILITY, DURATION AND SEVERITY.
Generally, NMOSD symptoms begin rapidly
After the initial attack, NMOSD follows an unpredictable course, and time to remission and relapse can vary
Recurring relapses can lead to an accumulation of disability over time
NMOSD IS MOST COMMONLY CHARACTERIZED BY

Rapid onset of eye pain or loss of vision (optic neuritis)
Limb weakness, numbness, or partial paralysis
Shooting pain or tingling in the neck, back, or abdomen
Loss of bowel and bladder control
Prolonged nausea, vomiting, or hiccups
ENDECE’S APPROACH
NDC-1308
NDC-1308 has a dual mechanism of action that may reduce inflammation and induce remyelination in neurodegenerative diseases such as Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder, which could effectively reverse the damage.
