WHAT IS A MACROPHAGE?

A macrophage is a type of white blood cell called a phagocyte. It is the first line of defense that cleans the body of bacteria and viruses called antigens.
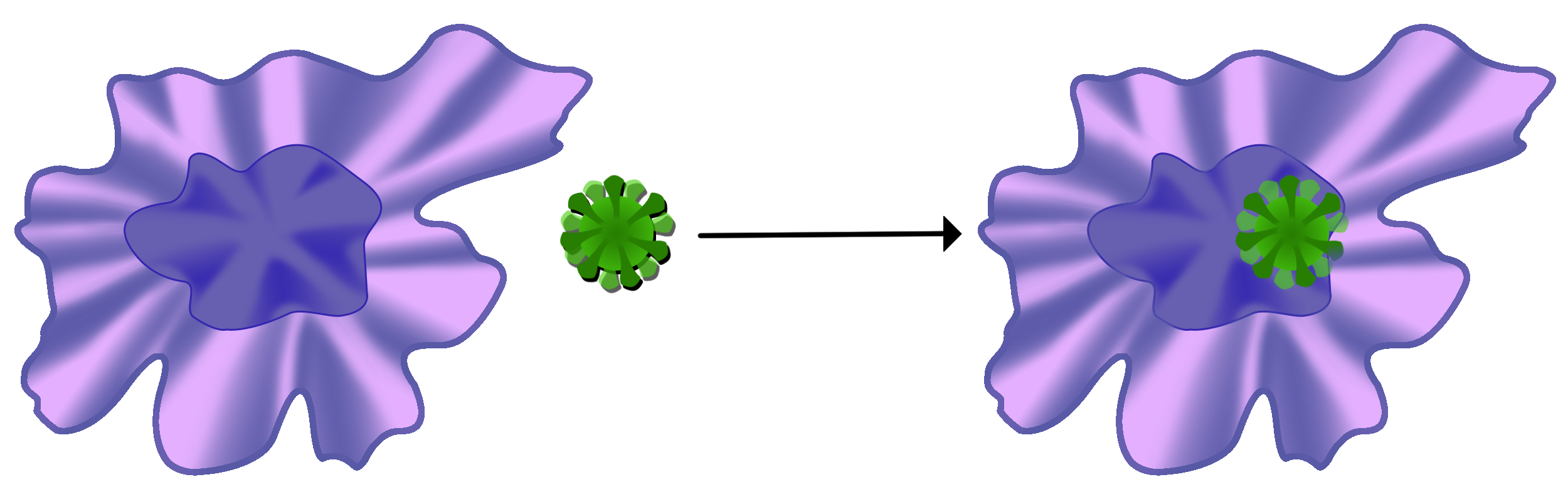
When a macrophage locates an antigen, it engulfs and destroys it.
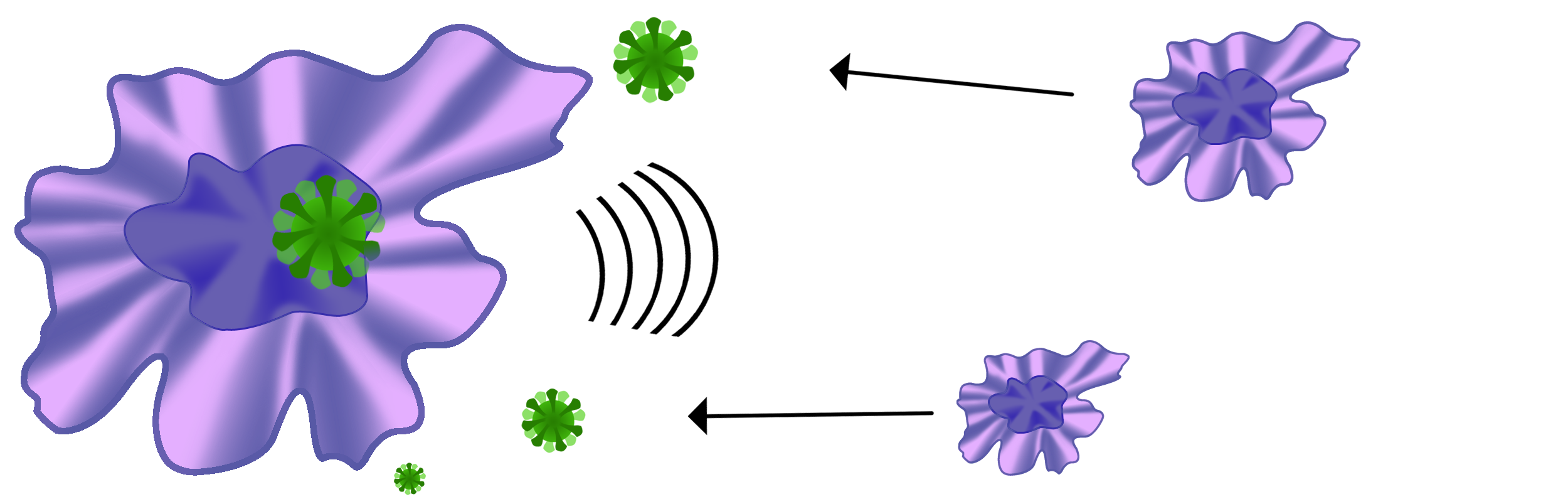
Upon being presented with numerous antigens, macrophages send out inflammatory signals that alert other macrophages to migrate to the area in order to help destroy the bacteria or virus.
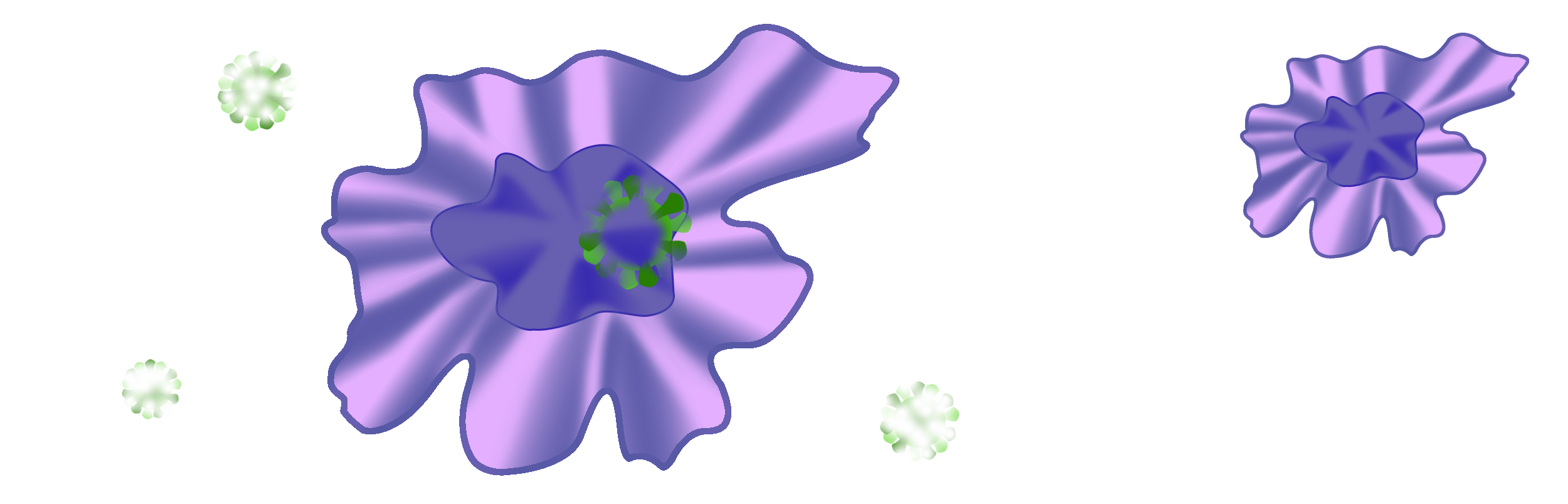
Normally when the antigens are destroyed, the macrophages stop producing inflammatory signals and return to a resting state.
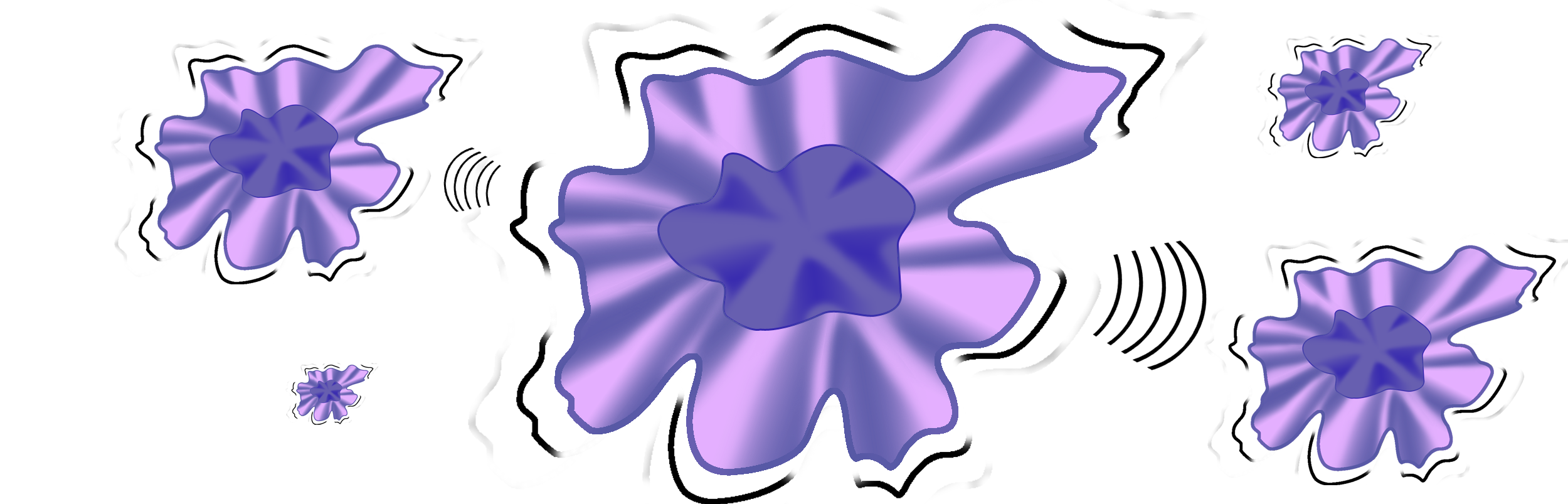
When macrophages do not return to their resting state after the antigens have been destroyed, and continue to produce inflammatory signals, the prolonged inflammation can lead progressively to respiratory distress, respiratory failure, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), and the Cytokine Storm, as well as death.
